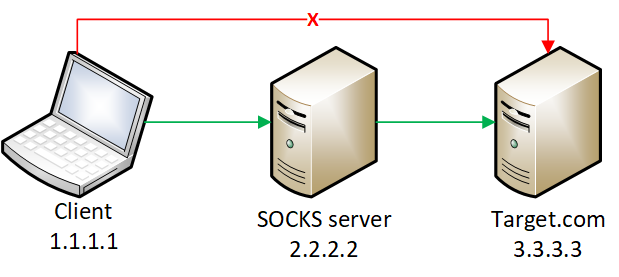
Suspicious Utility Launched via ProxyChains
This rule monitors for the execution of suspicious linux tools through ProxyChains. ProxyChains is a command-line tool that enables the routing of network connections through intermediary proxies, enhancing anonymity and enabling access to restricted resources. Attackers can exploit the ProxyChains utility to hide their true source IP address, evade detection, and perform malicious activities through a chain of proxy servers, potentially masking their identity and intentions.
Elastic rule (View on GitHub)
1[metadata]
2creation_date = "2023/08/23"
3integration = ["endpoint", "auditd_manager"]
4maturity = "production"
5updated_date = "2024/05/21"
6
7[transform]
8[[transform.osquery]]
9label = "Osquery - Retrieve Listening Ports"
10query = "SELECT pid, address, port, socket, protocol, path FROM listening_ports"
11
12[[transform.osquery]]
13label = "Osquery - Retrieve Open Sockets"
14query = "SELECT pid, family, remote_address, remote_port, socket, state FROM process_open_sockets"
15
16[[transform.osquery]]
17label = "Osquery - Retrieve Information for a Specific User"
18query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = {{user.name}}"
19
20[[transform.osquery]]
21label = "Osquery - Investigate the Account Authentication Status"
22query = "SELECT * FROM logged_in_users WHERE user = {{user.name}}"
23
24[[transform.osquery]]
25label = "Osquery - Retrieve Running Processes by User"
26query = "SELECT pid, username, name FROM processes p JOIN users u ON u.uid = p.uid ORDER BY username"
27
28[[transform.osquery]]
29label = "Osquery - Retrieve Process Info"
30query = "SELECT name, cmdline, parent, path, uid FROM processes"
31
32
33[rule]
34author = ["Elastic"]
35description = """
36This rule monitors for the execution of suspicious linux tools through ProxyChains. ProxyChains is a command-line tool
37that enables the routing of network connections through intermediary proxies, enhancing anonymity and enabling access to
38restricted resources. Attackers can exploit the ProxyChains utility to hide their true source IP address, evade
39detection, and perform malicious activities through a chain of proxy servers, potentially masking their identity and
40intentions.
41"""
42from = "now-9m"
43index = ["logs-endpoint.events.*", "endgame-*", "auditbeat-*", "logs-auditd_manager.auditd-*"]
44language = "eql"
45license = "Elastic License v2"
46name = "Suspicious Utility Launched via ProxyChains"
47note = """## Triage and analysis
48
49### Investigating Suspicious Utility Launched via ProxyChains
50
51Attackers can leverage `proxychains` to obfuscate their origin and bypass network defenses by routing their malicious traffic through multiple intermediary servers.
52
53This rule looks for a list of suspicious processes spawned through `proxychains` by analyzing process command line arguments.
54
55> **Note**:
56> This investigation guide uses the [Osquery Markdown Plugin](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/security/master/invest-guide-run-osquery.html) introduced in Elastic Stack version 8.5.0. Older Elastic Stack versions will display unrendered Markdown in this guide.
57> This investigation guide uses [placeholder fields](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/security/current/osquery-placeholder-fields.html) to dynamically pass alert data into Osquery queries. Placeholder fields were introduced in Elastic Stack version 8.7.0. If you're using Elastic Stack version 8.6.0 or earlier, you'll need to manually adjust this investigation guide's queries to ensure they properly run.
58
59#### Possible investigation steps
60
61- Identify any signs of suspicious network activity or anomalies that may indicate network obfuscation. This could include unexpected traffic patterns or unusual network behavior.
62 - Investigate listening ports and open sockets to look for potential protocol tunneling, reverse shells, or data exfiltration.
63 - $osquery_0
64 - $osquery_1
65- Identify the user account that performed the action, analyze it, and check whether it should perform this kind of action.
66 - $osquery_2
67- Investigate whether the user is currently logged in and active.
68 - $osquery_3
69- Investigate the script execution chain (parent process tree) for unknown processes. Examine their executable files for prevalence and whether they are located in expected locations.
70 - $osquery_4
71 - $osquery_5
72- Investigate other alerts associated with the user/host during the past 48 hours.
73 - If scripts or executables were dropped, retrieve the files and determine if they are malicious:
74 - Use a private sandboxed malware analysis system to perform analysis.
75 - Observe and collect information about the following activities:
76 - Attempts to contact external domains and addresses.
77 - Check if the domain is newly registered or unexpected.
78 - Check the reputation of the domain or IP address.
79 - File access, modification, and creation activities.
80
81### Related rules
82
83- ProxyChains Activity - 4b868f1f-15ff-4ba3-8c11-d5a7a6356d37
84- Potential Protocol Tunneling via Chisel Client - 3f12325a-4cc6-410b-8d4c-9fbbeb744cfd
85- Potential Protocol Tunneling via Chisel Server - ac8805f6-1e08-406c-962e-3937057fa86f
86- Potential Linux Tunneling and/or Port Forwarding - 6ee947e9-de7e-4281-a55d-09289bdf947e
87- Potential Protocol Tunneling via EarthWorm - 9f1c4ca3-44b5-481d-ba42-32dc215a2769
88
89### False positive analysis
90
91- If this activity is related to new benign software installation activity, consider adding exceptions — preferably with a combination of user and command line conditions.
92- If this activity is related to a system administrator or developer who uses this utility for benign purposes, consider adding exceptions for specific user accounts or hosts.
93- Try to understand the context of the execution by thinking about the user, machine, or business purpose. A small number of endpoints, such as servers with unique software, might appear unusual but satisfy a specific business need.
94
95### Response and remediation
96
97- Initiate the incident response process based on the outcome of the triage.
98- Isolate the involved host to prevent further post-compromise behavior.
99- If the triage identified malware, search the environment for additional compromised hosts.
100 - Implement temporary network rules, procedures, and segmentation to contain the malware.
101 - Stop suspicious processes.
102 - Immediately block the identified indicators of compromise (IoCs).
103 - Inspect the affected systems for additional malware backdoors, such as reverse shells, reverse proxies, or droppers, that attackers could use to reinfect the system.
104- Remove and block malicious artifacts identified during triage.
105- Investigate credential exposure on systems compromised or used by the attacker to ensure all compromised accounts are identified. Reset passwords for these accounts and other potentially compromised credentials, such as email, business systems, and web services.
106- Run a full antimalware scan. This may reveal additional artifacts left in the system, persistence mechanisms, and malware components.
107- Determine the initial vector abused by the attacker and take action to prevent reinfection through the same vector.
108- Leverage the incident response data and logging to improve the mean time to detect (MTTD) and the mean time to respond (MTTR).
109"""
110references = ["https://blog.bitsadmin.com/living-off-the-foreign-land-windows-as-offensive-platform"]
111risk_score = 21
112rule_id = "6ace94ba-f02c-4d55-9f53-87d99b6f9af4"
113setup = """## Setup
114
115This rule requires data coming in from Elastic Defend.
116
117### Elastic Defend Integration Setup
118Elastic Defend is integrated into the Elastic Agent using Fleet. Upon configuration, the integration allows the Elastic Agent to monitor events on your host and send data to the Elastic Security app.
119
120#### Prerequisite Requirements:
121- Fleet is required for Elastic Defend.
122- To configure Fleet Server refer to the [documentation](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/fleet/current/fleet-server.html).
123
124#### The following steps should be executed in order to add the Elastic Defend integration on a Linux System:
125- Go to the Kibana home page and click "Add integrations".
126- In the query bar, search for "Elastic Defend" and select the integration to see more details about it.
127- Click "Add Elastic Defend".
128- Configure the integration name and optionally add a description.
129- Select the type of environment you want to protect, either "Traditional Endpoints" or "Cloud Workloads".
130- Select a configuration preset. Each preset comes with different default settings for Elastic Agent, you can further customize these later by configuring the Elastic Defend integration policy. [Helper guide](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/security/current/configure-endpoint-integration-policy.html).
131- We suggest selecting "Complete EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response)" as a configuration setting, that provides "All events; all preventions"
132- Enter a name for the agent policy in "New agent policy name". If other agent policies already exist, you can click the "Existing hosts" tab and select an existing policy instead.
133For more details on Elastic Agent configuration settings, refer to the [helper guide](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/fleet/8.10/agent-policy.html).
134- Click "Save and Continue".
135- To complete the integration, select "Add Elastic Agent to your hosts" and continue to the next section to install the Elastic Agent on your hosts.
136For more details on Elastic Defend refer to the [helper guide](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/security/current/install-endpoint.html).
137"""
138severity = "low"
139tags = [
140 "Domain: Endpoint",
141 "OS: Linux",
142 "Use Case: Threat Detection",
143 "Tactic: Command and Control",
144 "Data Source: Elastic Defend",
145 "Data Source: Elastic Endgame",
146 "Data Source: Auditd Manager",
147]
148timestamp_override = "event.ingested"
149type = "eql"
150
151query = '''
152process where host.os.type == "linux" and event.type == "start" and event.action in ("exec", "exec_event", "executed", "process_started")
153 and process.name == "proxychains" and process.args : (
154 "ssh", "sshd", "sshuttle", "socat", "iodine", "iodined", "dnscat", "hans", "hans-ubuntu", "ptunnel-ng",
155 "ssf", "3proxy", "ngrok", "gost", "pivotnacci", "chisel*", "nmap", "ping", "python*", "php*", "perl", "ruby",
156 "lua*", "openssl", "nc", "netcat", "ncat", "telnet", "awk", "java", "telnet", "ftp", "curl", "wget"
157)
158'''
159
160
161[[rule.threat]]
162framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
163[[rule.threat.technique]]
164id = "T1572"
165name = "Protocol Tunneling"
166reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1572/"
167
168
169[rule.threat.tactic]
170id = "TA0011"
171name = "Command and Control"
172reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0011/"
Triage and analysis
Investigating Suspicious Utility Launched via ProxyChains
Attackers can leverage proxychains to obfuscate their origin and bypass network defenses by routing their malicious traffic through multiple intermediary servers.
This rule looks for a list of suspicious processes spawned through proxychains by analyzing process command line arguments.
Note: This investigation guide uses the Osquery Markdown Plugin introduced in Elastic Stack version 8.5.0. Older Elastic Stack versions will display unrendered Markdown in this guide. This investigation guide uses placeholder fields to dynamically pass alert data into Osquery queries. Placeholder fields were introduced in Elastic Stack version 8.7.0. If you're using Elastic Stack version 8.6.0 or earlier, you'll need to manually adjust this investigation guide's queries to ensure they properly run.
Possible investigation steps
- Identify any signs of suspicious network activity or anomalies that may indicate network obfuscation. This could include unexpected traffic patterns or unusual network behavior.
- Investigate listening ports and open sockets to look for potential protocol tunneling, reverse shells, or data exfiltration.
- $osquery_0
- $osquery_1
- Investigate listening ports and open sockets to look for potential protocol tunneling, reverse shells, or data exfiltration.
- Identify the user account that performed the action, analyze it, and check whether it should perform this kind of action.
- $osquery_2
- Investigate whether the user is currently logged in and active.
- $osquery_3
- Investigate the script execution chain (parent process tree) for unknown processes. Examine their executable files for prevalence and whether they are located in expected locations.
- $osquery_4
- $osquery_5
- Investigate other alerts associated with the user/host during the past 48 hours.
- If scripts or executables were dropped, retrieve the files and determine if they are malicious:
- Use a private sandboxed malware analysis system to perform analysis.
- Observe and collect information about the following activities:
- Attempts to contact external domains and addresses.
- Check if the domain is newly registered or unexpected.
- Check the reputation of the domain or IP address.
- File access, modification, and creation activities.
- Attempts to contact external domains and addresses.
- Observe and collect information about the following activities:
- Use a private sandboxed malware analysis system to perform analysis.
- If scripts or executables were dropped, retrieve the files and determine if they are malicious:
Related rules
- ProxyChains Activity - 4b868f1f-15ff-4ba3-8c11-d5a7a6356d37
- Potential Protocol Tunneling via Chisel Client - 3f12325a-4cc6-410b-8d4c-9fbbeb744cfd
- Potential Protocol Tunneling via Chisel Server - ac8805f6-1e08-406c-962e-3937057fa86f
- Potential Linux Tunneling and/or Port Forwarding - 6ee947e9-de7e-4281-a55d-09289bdf947e
- Potential Protocol Tunneling via EarthWorm - 9f1c4ca3-44b5-481d-ba42-32dc215a2769
False positive analysis
- If this activity is related to new benign software installation activity, consider adding exceptions — preferably with a combination of user and command line conditions.
- If this activity is related to a system administrator or developer who uses this utility for benign purposes, consider adding exceptions for specific user accounts or hosts.
- Try to understand the context of the execution by thinking about the user, machine, or business purpose. A small number of endpoints, such as servers with unique software, might appear unusual but satisfy a specific business need.
Response and remediation
- Initiate the incident response process based on the outcome of the triage.
- Isolate the involved host to prevent further post-compromise behavior.
- If the triage identified malware, search the environment for additional compromised hosts.
- Implement temporary network rules, procedures, and segmentation to contain the malware.
- Stop suspicious processes.
- Immediately block the identified indicators of compromise (IoCs).
- Inspect the affected systems for additional malware backdoors, such as reverse shells, reverse proxies, or droppers, that attackers could use to reinfect the system.
- Remove and block malicious artifacts identified during triage.
- Investigate credential exposure on systems compromised or used by the attacker to ensure all compromised accounts are identified. Reset passwords for these accounts and other potentially compromised credentials, such as email, business systems, and web services.
- Run a full antimalware scan. This may reveal additional artifacts left in the system, persistence mechanisms, and malware components.
- Determine the initial vector abused by the attacker and take action to prevent reinfection through the same vector.
- Leverage the incident response data and logging to improve the mean time to detect (MTTD) and the mean time to respond (MTTR).
References
Related rules
- ProxyChains Activity
- Attempt to Clear Kernel Ring Buffer
- Base16 or Base32 Encoding/Decoding Activity
- ESXI Discovery via Find
- ESXI Discovery via Grep