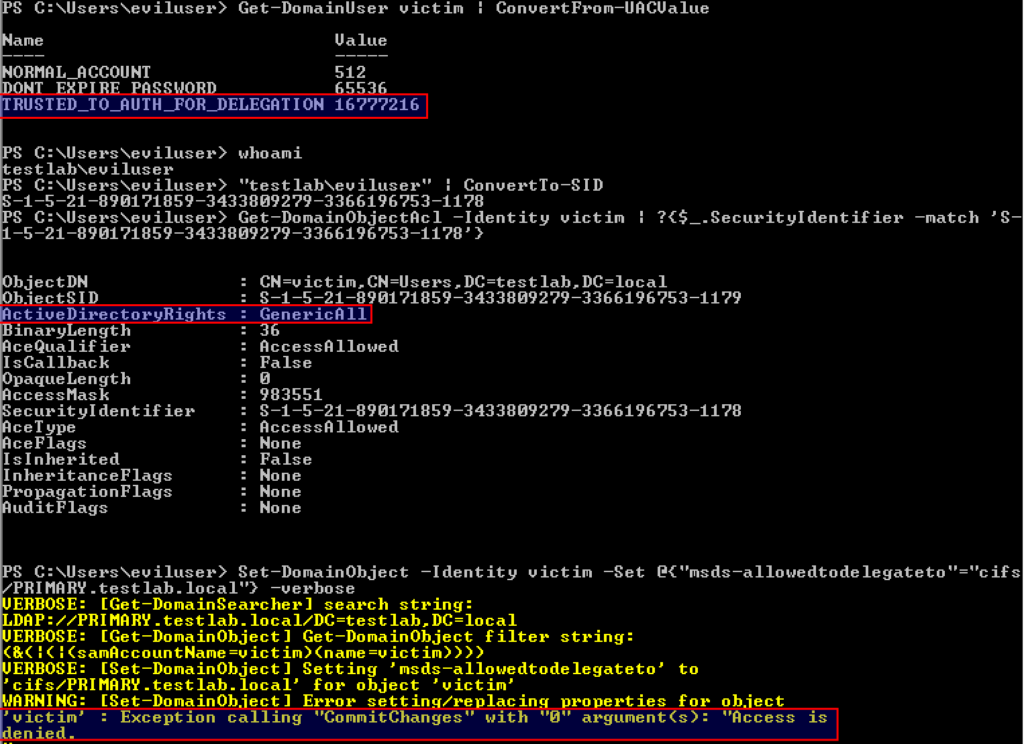
Sensitive Privilege SeEnableDelegationPrivilege assigned to a User
Identifies the assignment of the SeEnableDelegationPrivilege sensitive "user right" to a user. The SeEnableDelegationPrivilege "user right" enables computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation. Attackers can abuse this right to compromise Active Directory accounts and elevate their privileges.
Elastic rule (View on GitHub)
1[metadata]
2creation_date = "2022/01/27"
3integration = ["system", "windows"]
4maturity = "production"
5updated_date = "2024/05/21"
6
7[rule]
8author = ["Elastic"]
9description = """
10Identifies the assignment of the SeEnableDelegationPrivilege sensitive "user right" to a user. The
11SeEnableDelegationPrivilege "user right" enables computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation. Attackers can
12abuse this right to compromise Active Directory accounts and elevate their privileges.
13"""
14from = "now-9m"
15index = ["winlogbeat-*", "logs-system.*", "logs-windows.*"]
16language = "kuery"
17license = "Elastic License v2"
18name = "Sensitive Privilege SeEnableDelegationPrivilege assigned to a User"
19note = """## Triage and analysis
20
21### Investigating Sensitive Privilege SeEnableDelegationPrivilege assigned to a User
22
23Kerberos delegation is an Active Directory feature that allows user and computer accounts to impersonate other accounts, act on their behalf, and use their privileges. Delegation (constrained and unconstrained) can be configured for user and computer objects.
24
25Enabling unconstrained delegation for a computer causes the computer to store the ticket-granting ticket (TGT) in memory at any time an account connects to the computer, so it can be used by the computer for impersonation when needed. Risk is heightened if an attacker compromises computers with unconstrained delegation enabled, as they could extract TGTs from memory and then replay them to move laterally on the domain. If the attacker coerces a privileged user to connect to the server, or if the user does so routinely, the account will be compromised and the attacker will be able to pass-the-ticket to privileged assets.
26
27SeEnableDelegationPrivilege is a user right that is controlled within the Local Security Policy of a domain controller and is managed through Group Policy. This setting is named **Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation**.
28
29It is critical to control the assignment of this privilege. A user with this privilege and write access to a computer can control delegation settings, perform the attacks described above, and harvest TGTs from any user that connects to the system.
30
31#### Possible investigation steps
32
33- Investigate how the privilege was assigned to the user and who assigned it.
34- Investigate other potentially malicious activity that was performed by the user that assigned the privileges using the `user.id` and `winlog.activity_id` fields as a filter during the past 48 hours.
35- Investigate other alerts associated with the users/host during the past 48 hours.
36
37### False positive analysis
38
39- The SeEnableDelegationPrivilege privilege should not be assigned to users. If this rule is triggered in your environment legitimately, the security team should notify the administrators about the risks of using it.
40
41### Related rules
42
43- KRBTGT Delegation Backdoor - e052c845-48d0-4f46-8a13-7d0aba05df82
44
45### Response and remediation
46
47- Initiate the incident response process based on the outcome of the triage.
48- Remove the privilege from the account.
49- Review the privileges of the administrator account that performed the action.
50- Determine the initial vector abused by the attacker and take action to prevent reinfection through the same vector.
51- Using the incident response data, update logging and audit policies to improve the mean time to detect (MTTD) and the mean time to respond (MTTR).
52"""
53references = [
54 "https://blog.harmj0y.net/activedirectory/the-most-dangerous-user-right-you-probably-have-never-heard-of/",
55 "https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma/blob/master/rules/windows/builtin/security/win_alert_active_directory_user_control.yml",
56 "https://twitter.com/_nwodtuhs/status/1454049485080907776",
57 "https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/kerberos/delegations",
58 "https://github.com/atc-project/atomic-threat-coverage/blob/master/Atomic_Threat_Coverage/Logging_Policies/LP_0105_windows_audit_authorization_policy_change.md",
59]
60risk_score = 73
61rule_id = "f494c678-3c33-43aa-b169-bb3d5198c41d"
62setup = """## Setup
63
64The 'Audit Authorization Policy Change' logging policy must be configured for (Success, Failure).
65Steps to implement the logging policy with Advanced Audit Configuration:
Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies > Policy Change > Audit Authorization Policy Change (Success,Failure)
1"""
2severity = "high"
3tags = [
4 "Domain: Endpoint",
5 "OS: Windows",
6 "Use Case: Threat Detection",
7 "Tactic: Credential Access",
8 "Tactic: Persistence",
9 "Data Source: Active Directory",
10 "Resources: Investigation Guide",
11 "Use Case: Active Directory Monitoring",
12]
13timestamp_override = "event.ingested"
14type = "query"
15
16query = '''
17event.action:"Authorization Policy Change" and event.code:4704 and
18 winlog.event_data.PrivilegeList:"SeEnableDelegationPrivilege"
19'''
20
21
22[[rule.threat]]
23framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
24[[rule.threat.technique]]
25id = "T1558"
26name = "Steal or Forge Kerberos Tickets"
27reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1558/"
28
29
30[rule.threat.tactic]
31id = "TA0006"
32name = "Credential Access"
33reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0006/"
34[[rule.threat]]
35framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
36[[rule.threat.technique]]
37id = "T1098"
38name = "Account Manipulation"
39reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1098/"
40
41
42[rule.threat.tactic]
43id = "TA0003"
44name = "Persistence"
45reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0003/"
Triage and analysis
Investigating Sensitive Privilege SeEnableDelegationPrivilege assigned to a User
Kerberos delegation is an Active Directory feature that allows user and computer accounts to impersonate other accounts, act on their behalf, and use their privileges. Delegation (constrained and unconstrained) can be configured for user and computer objects.
Enabling unconstrained delegation for a computer causes the computer to store the ticket-granting ticket (TGT) in memory at any time an account connects to the computer, so it can be used by the computer for impersonation when needed. Risk is heightened if an attacker compromises computers with unconstrained delegation enabled, as they could extract TGTs from memory and then replay them to move laterally on the domain. If the attacker coerces a privileged user to connect to the server, or if the user does so routinely, the account will be compromised and the attacker will be able to pass-the-ticket to privileged assets.
SeEnableDelegationPrivilege is a user right that is controlled within the Local Security Policy of a domain controller and is managed through Group Policy. This setting is named Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation.
It is critical to control the assignment of this privilege. A user with this privilege and write access to a computer can control delegation settings, perform the attacks described above, and harvest TGTs from any user that connects to the system.
Possible investigation steps
- Investigate how the privilege was assigned to the user and who assigned it.
- Investigate other potentially malicious activity that was performed by the user that assigned the privileges using the
user.idandwinlog.activity_idfields as a filter during the past 48 hours. - Investigate other alerts associated with the users/host during the past 48 hours.
False positive analysis
- The SeEnableDelegationPrivilege privilege should not be assigned to users. If this rule is triggered in your environment legitimately, the security team should notify the administrators about the risks of using it.
Related rules
- KRBTGT Delegation Backdoor - e052c845-48d0-4f46-8a13-7d0aba05df82
Response and remediation
- Initiate the incident response process based on the outcome of the triage.
- Remove the privilege from the account.
- Review the privileges of the administrator account that performed the action.
- Determine the initial vector abused by the attacker and take action to prevent reinfection through the same vector.
- Using the incident response data, update logging and audit policies to improve the mean time to detect (MTTD) and the mean time to respond (MTTR).
References
Related rules
- Account Configured with Never-Expiring Password
- FirstTime Seen Account Performing DCSync
- Kerberos Pre-authentication Disabled for User
- Potential Credential Access via DCSync
- Suspicious Remote Registry Access via SeBackupPrivilege