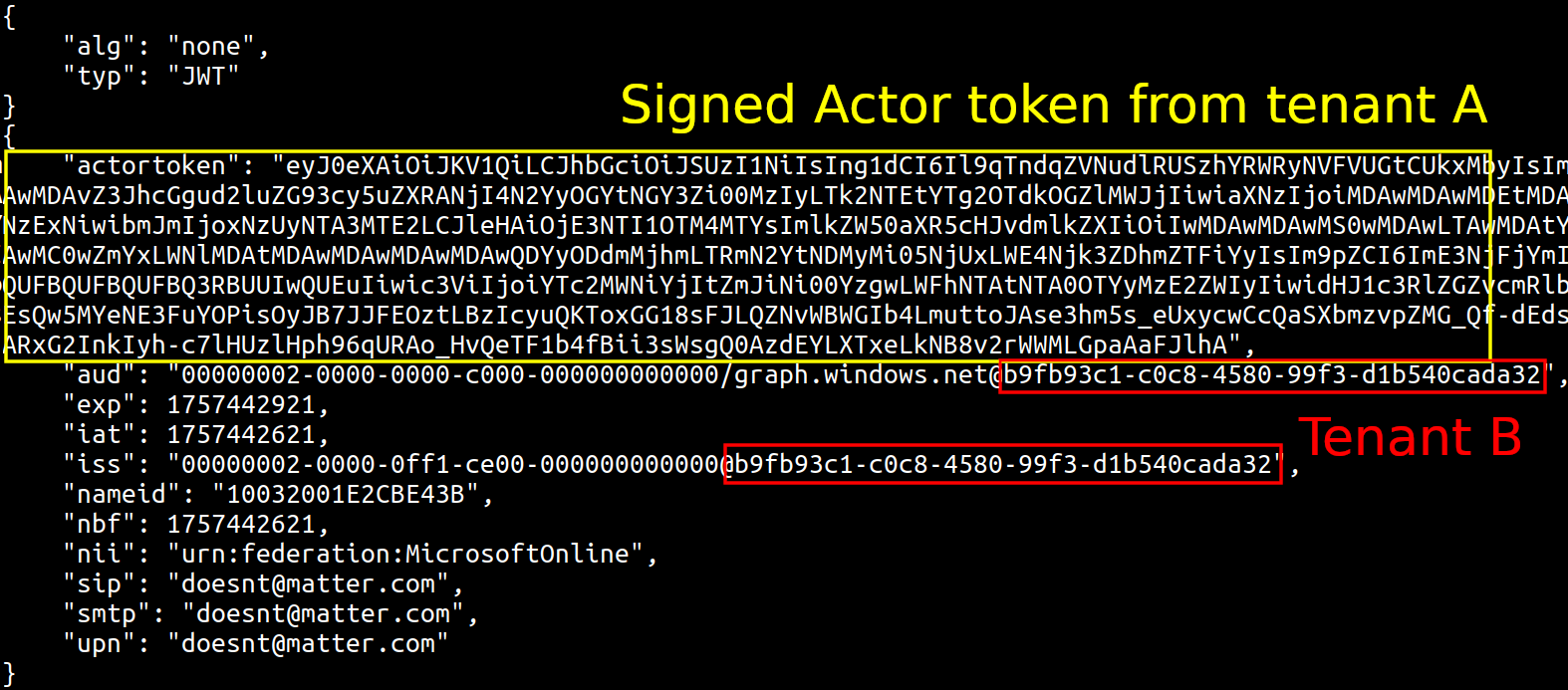
Entra ID Actor Token User Impersonation Abuse
Identifies potential abuse of actor tokens in Microsoft Entra ID audit logs. Actor tokens are undocumented backend mechanisms used by Microsoft for service-to-service (S2S) operations, allowing services to perform actions on behalf of users. These tokens appear in logs with the service's display name but the impersonated user's UPN. While some legitimate Microsoft operations use actor tokens, unexpected usage may indicate exploitation of CVE-2025-55241, which allowed unauthorized access to Azure AD Graph API across tenants before being patched by Microsoft.
Elastic rule (View on GitHub)
1[metadata]
2creation_date = "2025/09/18"
3integration = ["azure"]
4maturity = "production"
5updated_date = "2025/12/09"
6
7[rule]
8author = ["Elastic"]
9description = """
10Identifies potential abuse of actor tokens in Microsoft Entra ID audit logs. Actor tokens are undocumented backend
11mechanisms used by Microsoft for service-to-service (S2S) operations, allowing services to perform actions on behalf
12of users. These tokens appear in logs with the service's display name but the impersonated user's UPN. While some
13legitimate Microsoft operations use actor tokens, unexpected usage may indicate exploitation of CVE-2025-55241, which
14allowed unauthorized access to Azure AD Graph API across tenants before being patched by Microsoft.
15"""
16false_positives = [
17 """
18 Creating specific groups via the Exchange Online PowerShell module will make Exchange use an Actor token on your
19 behalf. The rule excludes group operations and directory feature operations to reduce false positives from these
20 legitimate administrative activities.
21 """,
22]
23from = "now-9m"
24interval = "8m"
25language = "esql"
26license = "Elastic License v2"
27name = "Entra ID Actor Token User Impersonation Abuse"
28note = """## Triage and analysis
29
30### Investigating Entra ID Actor Token User Impersonation Abuse
31
32This rule detects when Microsoft services use actor tokens to perform operations in audit logs. Actor tokens are undocumented backend mechanisms used by Microsoft for service-to-service (S2S) communication. They appear with a mismatch: the service's display name but the impersonated user's UPN. While some operations legitimately use actor tokens, unexpected usage may indicate exploitation of CVE-2025-55241, which allowed attackers to obtain Global Admin privileges across any Entra ID tenant. Note that this vulnerability has been patched by Microsoft as of September 2025.
33
34### Possible investigation steps
35
36- Review the `azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.userPrincipalName` field to identify which service principals are exhibiting this behavior.
37- Check the `azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.displayName` to confirm these are legitimate Microsoft services.
38- Analyze the actions performed by these service principals - look for privilege escalations, permission grants, or unusual administrative operations.
39- Review the timing and frequency of these events to identify potential attack patterns or automated exploitation.
40- Cross-reference with recent administrative changes or service configurations that might explain legitimate use cases.
41- Check if any new applications or service principals were registered recently that could be related to this activity.
42- Investigate any correlation with other suspicious authentication events or privilege escalation attempts in your tenant.
43
44### False positive analysis
45
46- Legitimate Microsoft service migrations or updates may temporarily exhibit this behavior.
47- Third-party integrations using Microsoft Graph or other APIs might trigger this pattern during normal operations.
48- Automated administrative tools or scripts using service principal authentication could be misconfigured.
49
50### Response and remediation
51
52- Immediately review and audit all service principal permissions and recent consent grants in your Entra ID tenant.
53- Disable or restrict any suspicious service principals exhibiting this behavior until verified.
54- Review and revoke any unnecessary application permissions, especially those with high privileges.
55- Enable and review Entra ID audit logs for any permission grants or role assignments made by these service principals.
56- Implement Conditional Access policies to restrict service principal authentication from unexpected locations or conditions.
57- Enable Entra ID Identity Protection to detect and respond to risky service principal behaviors.
58- Review and harden application consent policies to prevent unauthorized service principal registrations.
59- Consider implementing privileged identity management (PIM) for service principal role assignments.
60"""
61references = [
62 "https://dirkjanm.io/obtaining-global-admin-in-every-entra-id-tenant-with-actor-tokens/",
63 "https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/advisory/CVE-2025-55241"
64]
65risk_score = 47
66rule_id = "8e7a4f2c-9b3d-4e5a-a1b6-c2d8f7e9b3a5"
67severity = "medium"
68tags = [
69 "Domain: Cloud",
70 "Domain: Identity",
71 "Data Source: Azure",
72 "Data Source: Entra ID",
73 "Data Source: Entra Audit Logs",
74 "Use Case: Identity and Access Audit",
75 "Use Case: Threat Detection",
76 "Tactic: Initial Access",
77 "Tactic: Privilege Escalation",
78 "Resources: Investigation Guide",
79]
80timestamp_override = "event.ingested"
81type = "esql"
82
83query = '''
84from logs-azure.auditlogs-* metadata _id, _version, _index
85| where azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.displayName in (
86 "Office 365 Exchange Online",
87 "Skype for Business Online",
88 "Dataverse",
89 "Office 365 SharePoint Online",
90 "Microsoft Dynamics ERP"
91 ) and
92 not azure.auditlogs.operation_name like "*group*" and
93 azure.auditlogs.operation_name != "Set directory feature on tenant"
94 and azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.userPrincipalName rlike ".+@[A-Za-z0-9.]+\\.[A-Za-z]{2,}"
95| keep
96 @timestamp,
97 azure.*,
98 client.*,
99 event.*,
100 source.*,
101 _id,
102 _version,
103 _index
104'''
105
106
107[[rule.threat]]
108framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
109[[rule.threat.technique]]
110id = "T1078"
111name = "Valid Accounts"
112reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1078/"
113[[rule.threat.technique.subtechnique]]
114id = "T1078.004"
115name = "Cloud Accounts"
116reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1078/004/"
117
118
119
120[rule.threat.tactic]
121id = "TA0001"
122name = "Initial Access"
123reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0001/"
124[[rule.threat]]
125framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
126[[rule.threat.technique]]
127id = "T1548"
128name = "Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism"
129reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1548/"
130
131
132[rule.threat.tactic]
133id = "TA0004"
134name = "Privilege Escalation"
135reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0004/"
Triage and analysis
Investigating Entra ID Actor Token User Impersonation Abuse
This rule detects when Microsoft services use actor tokens to perform operations in audit logs. Actor tokens are undocumented backend mechanisms used by Microsoft for service-to-service (S2S) communication. They appear with a mismatch: the service's display name but the impersonated user's UPN. While some operations legitimately use actor tokens, unexpected usage may indicate exploitation of CVE-2025-55241, which allowed attackers to obtain Global Admin privileges across any Entra ID tenant. Note that this vulnerability has been patched by Microsoft as of September 2025.
Possible investigation steps
- Review the
azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.userPrincipalNamefield to identify which service principals are exhibiting this behavior. - Check the
azure.auditlogs.properties.initiated_by.user.displayNameto confirm these are legitimate Microsoft services. - Analyze the actions performed by these service principals - look for privilege escalations, permission grants, or unusual administrative operations.
- Review the timing and frequency of these events to identify potential attack patterns or automated exploitation.
- Cross-reference with recent administrative changes or service configurations that might explain legitimate use cases.
- Check if any new applications or service principals were registered recently that could be related to this activity.
- Investigate any correlation with other suspicious authentication events or privilege escalation attempts in your tenant.
False positive analysis
- Legitimate Microsoft service migrations or updates may temporarily exhibit this behavior.
- Third-party integrations using Microsoft Graph or other APIs might trigger this pattern during normal operations.
- Automated administrative tools or scripts using service principal authentication could be misconfigured.
Response and remediation
- Immediately review and audit all service principal permissions and recent consent grants in your Entra ID tenant.
- Disable or restrict any suspicious service principals exhibiting this behavior until verified.
- Review and revoke any unnecessary application permissions, especially those with high privileges.
- Enable and review Entra ID audit logs for any permission grants or role assignments made by these service principals.
- Implement Conditional Access policies to restrict service principal authentication from unexpected locations or conditions.
- Enable Entra ID Identity Protection to detect and respond to risky service principal behaviors.
- Review and harden application consent policies to prevent unauthorized service principal registrations.
- Consider implementing privileged identity management (PIM) for service principal role assignments.
References
Related rules
- Entra ID Protection Admin Confirmed Compromise
- M365 Identity Login from Atypical Travel Location
- M365 Identity Login from Impossible Travel Location
- Deprecated - Azure Entra Sign-in Brute Force Microsoft 365 Accounts by Repeat Source
- Azure RBAC Built-In Administrator Roles Assigned