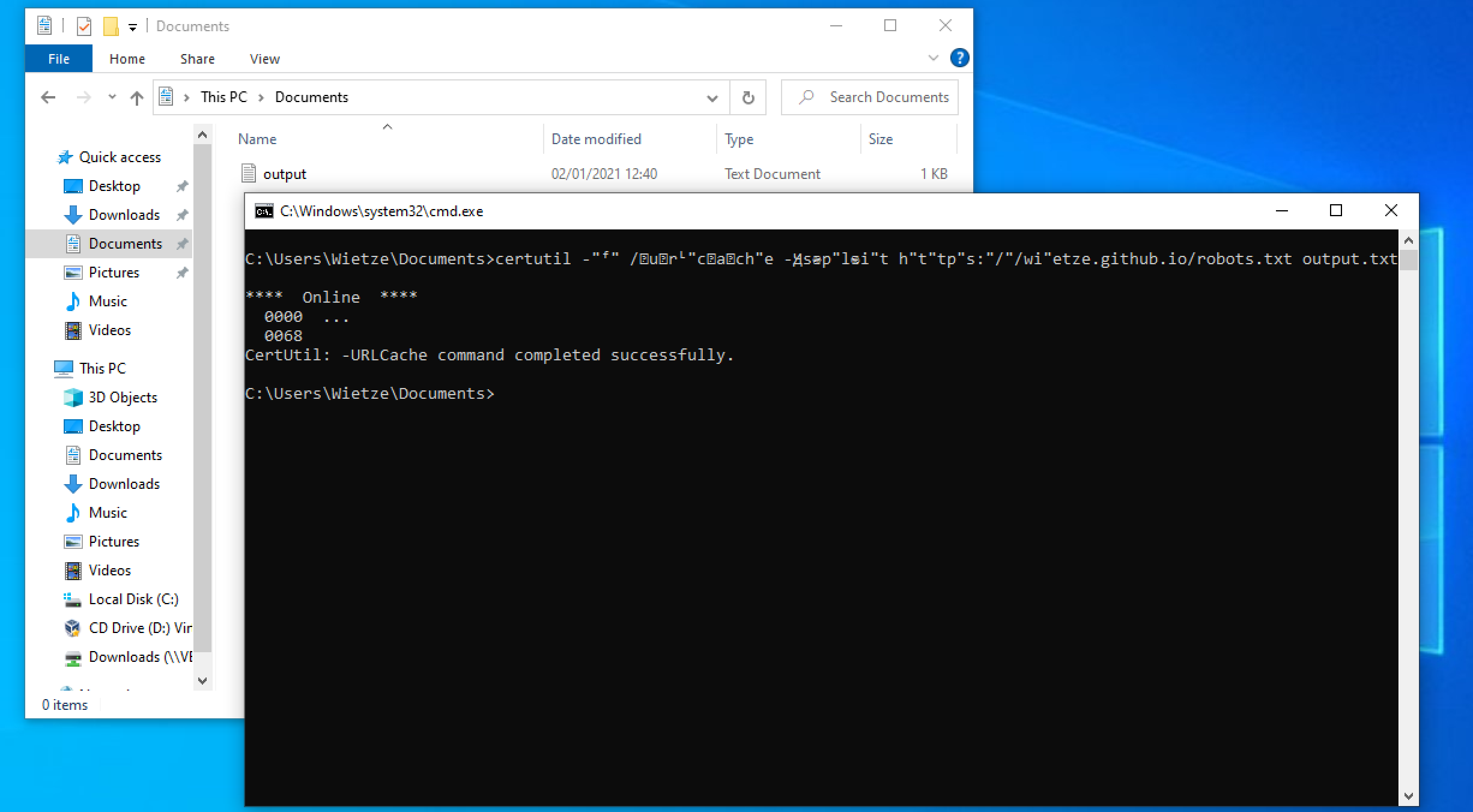
Command Obfuscation via Unicode Modifier Letters
Identifies the presence of unicode modifier letters in the process command_line. Adversaries sometimes replace ASCII characters with visually similar Unicode modifier letters or combining marks to evade simple string-based detections.
Elastic rule (View on GitHub)
1[metadata]
2creation_date = "2025/11/13"
3integration = ["endpoint", "windows", "system", "m365_defender", "sentinel_one_cloud_funnel", "crowdstrike"]
4maturity = "production"
5updated_date = "2025/11/13"
6
7[rule]
8author = ["Elastic"]
9description = """
10Identifies the presence of unicode modifier letters in the process command_line. Adversaries sometimes replace ASCII characters
11with visually similar Unicode modifier letters or combining marks to evade simple string-based detections.
12"""
13from = "now-9m"
14index = [
15 "endgame-*",
16 "logs-crowdstrike.fdr*",
17 "logs-endpoint.events.process-*",
18 "logs-m365_defender.event-*",
19 "logs-sentinel_one_cloud_funnel.*",
20 "logs-system.security*",
21 "logs-windows.forwarded*",
22 "logs-windows.sysmon_operational-*",
23 "winlogbeat-*",
24]
25language = "eql"
26license = "Elastic License v2"
27name = "Command Obfuscation via Unicode Modifier Letters"
28note = """ ## Triage and analysis
29
30> **Disclaimer**:
31> This investigation guide was created using generative AI technology and has been reviewed to improve its accuracy and relevance. While every effort has been made to ensure its quality, we recommend validating the content and adapting it to suit your specific environment and operational needs.
32
33### Investigating Command Obfuscation via Unicode Modifier Letters
34
35Adversaries sometimes replace ASCII characters with visually similar Unicode modifier letters or combining marks to evade simple string-based detections.
36
37### Possible investigation steps
38
39- Review the process execution details (command_line, parent, code signature, hash).
40- Analyze the full execution process tree to identify the root cause.
41- Check the creation of any persistence using scheduled tasks, Run key, services, shortcuts or startup folders.
42- Cross-reference with other logs or alerts to identify any related incidents or patterns of activity that might indicate a larger threat campaign.
43
44### False positive analysis
45
46- Legitimate internationalized applications and installers use Unicode (e.g., localized product names, non-Latin scripts).
47- Dev tools or fonts may create commands with combining marks (rare) — check installer/tool provenance.
48- Command lines that include user input, file names, or paths with non-ASCII characters (e.g., user folders) can trigger the rule.
49
50### Response and remediation
51
52- Isolate the host if there are signs of active compromise (outbound C2, credential theft, lateral movement).
53- Terminate the suspicious process and any direct descendants after collecting forensic evidence (memory, artifacts).
54- Collect EDR snapshots, full disk image or targeted file copies, registry hives, and network logs for investigation.
55- Remove any persistence entries (scheduled task, startup, services) tied to the activity.
56- Qurantine and submit samples to malware analysis; if confirmed malicious, remove and restore from known good backups.
57- Block and update indicators related to this activity (hashes, exact normalized command patterns, codepoint sequences, IPs/domains).
58- Run global hutning queries for same Unicode patterns, normalized variants, and identical parent/child process chains.
59"""
60references = ["https://www.wietzebeukema.nl/blog/windows-command-line-obfuscation"]
61risk_score = 73
62rule_id = "37148ae6-c6ec-4fe4-88b1-02f40aed93a9"
63severity = "high"
64tags = [
65 "Domain: Endpoint",
66 "OS: Windows",
67 "Use Case: Threat Detection",
68 "Tactic: Defense Evasion",
69 "Data Source: Elastic Endgame",
70 "Resources: Investigation Guide",
71 "Data Source: Elastic Defend",
72 "Data Source: Windows Security Event Logs",
73 "Data Source: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint",
74 "Data Source: Sysmon",
75 "Data Source: SentinelOne",
76 "Data Source: Crowdstrike",
77]
78timestamp_override = "event.ingested"
79type = "eql"
80
81query = '''
82process where host.os.type == "windows" and event.type == "start" and
83 (
84 process.name : ("reg.exe", "net.exe", "net1.exe", "certutil.exe", "MSHTA.EXE", "msiexec.exe", "bitsadmin.exe", "CertReq.exe", "PrintBrm.exe", "MSBuild.exe", "wuauclt.exe", "curl.exe", "wget.exe", "ssh.exe", "Cmd.Exe", "PowerShell.EX", "CONHOST.EXE", "wscript.exe", "cscript.exe", "REGSVR32.EXE", "RUNDLL32.EXE", "procdump.exe", "ntdsutil.exe", "diskshadow.exe", "schtasks.exe", "sc.exe", "wmic.exe", "VSSADMIN.EXE", "WBADMIN.EXE", "iCACLS.EXE", "sftp.exe", "scp.exe", "esentutl.exe", "InstallUtil.exe", "wevtutil.exe") or
85 ?process.pe.original_file_name in ("reg.exe", "net.exe", "net1.exe", "CertUtil.exe", "MSHTA.EXE", "msiexec.exe", "bitsadmin.exe", "CertReq.exe", "PrintBrm.exe", "MSBuild.exe", "wuauclt.exe", "curl.exe", "wget.exe", "ssh.exe", "Cmd.Exe", "PowerShell.EX", "CONHOST.EXE", "wscript.exe", "cscript.exe", "REGSVR32.EXE", "RUNDLL32.EXE", "procdump", "ntdsutil.exe", "diskshadow.exe", "schtasks.exe", "sc.exe", "wmic.exe", "VSSADMIN.EXE", "WBADMIN.EXE", "iCACLS.EXE", "sftp.exe", "scp.exe", "esentutl.exe", "InstallUtil.exe", "wevtutil.exe")
86 ) and
87 process.command_line regex """.*[ʰ-˿ᴬ-ᶻ]+.*"""
88'''
89
90
91[[rule.threat]]
92framework = "MITRE ATT&CK"
93[[rule.threat.technique]]
94id = "T1027"
95name = "Obfuscated Files or Information"
96reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1027/"
97
98[[rule.threat.technique.subtechnique]]
99id = "T1027.010"
100name = "Command Obfuscation"
101reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1027/010/"
102
103[rule.threat.tactic]
104id = "TA0005"
105name = "Defense Evasion"
106reference = "https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0005/"
Triage and analysis
Disclaimer: This investigation guide was created using generative AI technology and has been reviewed to improve its accuracy and relevance. While every effort has been made to ensure its quality, we recommend validating the content and adapting it to suit your specific environment and operational needs.
Investigating Command Obfuscation via Unicode Modifier Letters
Adversaries sometimes replace ASCII characters with visually similar Unicode modifier letters or combining marks to evade simple string-based detections.
Possible investigation steps
- Review the process execution details (command_line, parent, code signature, hash).
- Analyze the full execution process tree to identify the root cause.
- Check the creation of any persistence using scheduled tasks, Run key, services, shortcuts or startup folders.
- Cross-reference with other logs or alerts to identify any related incidents or patterns of activity that might indicate a larger threat campaign.
False positive analysis
- Legitimate internationalized applications and installers use Unicode (e.g., localized product names, non-Latin scripts).
- Dev tools or fonts may create commands with combining marks (rare) — check installer/tool provenance.
- Command lines that include user input, file names, or paths with non-ASCII characters (e.g., user folders) can trigger the rule.
Response and remediation
- Isolate the host if there are signs of active compromise (outbound C2, credential theft, lateral movement).
- Terminate the suspicious process and any direct descendants after collecting forensic evidence (memory, artifacts).
- Collect EDR snapshots, full disk image or targeted file copies, registry hives, and network logs for investigation.
- Remove any persistence entries (scheduled task, startup, services) tied to the activity.
- Qurantine and submit samples to malware analysis; if confirmed malicious, remove and restore from known good backups.
- Block and update indicators related to this activity (hashes, exact normalized command patterns, codepoint sequences, IPs/domains).
- Run global hutning queries for same Unicode patterns, normalized variants, and identical parent/child process chains.
References
Related rules
- Bypass UAC via Event Viewer
- Clearing Windows Event Logs
- Disable Windows Event and Security Logs Using Built-in Tools
- Disabling Windows Defender Security Settings via PowerShell
- Windows Defender Exclusions Added via PowerShell